Process Drone Data
Not Lite
Process Drone Data command provides a wizard for processing point clouds collected with UAV-mounted scanners. The wizard performs processing steps that are common for many different end products produced from point clouds. Basically, it combines automatic processing routines of TerraScan with pre-defined settings. The settings are optimized based on example data sets and can be adjusted, if necessary. The user may run all steps of the wizard or only selected steps at once. Manual processing tasks, such as checks, additional classification or other manipulation of the point cloud can be done at any point between the steps of the wizard.
Before running the wizard, a new UAV project must be created or points must be loaded into TerraScan. The wizard steps expect that the default point classes of TerraScan are available. The corresponding class file can be copied for a UAV project as part of the new project data import. From this class file, do not change classes with numbers 1-8 because they are considered as industry standard. Classes with class number 9 or higher may be modified according to project requirements. Some wizard steps require trajectory information. The trajectory files are created and provided automatically as part of the new project data import. Alternatively, they can be imported or loaded into TerraScan manually.
To create a process UAV point clouds automatically:
1. Select Process Drone Data command from the Wizard menu.
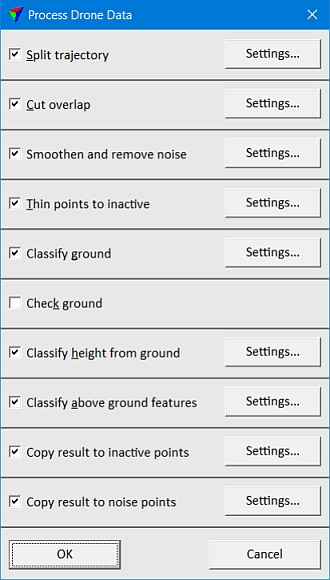
This opens the Process Drone Data dialog:
2. Switch on the processing steps you want to apply.
3. For each processing step, click on the Settings button in order to check and possibly adjust the settings.
4. Click OK.
Split trajectory step cuts the trajectory covering the data collection area into separate flight paths. As a result, data from the different flight paths can be easily compared and overlap between data collected in different flight paths can be removed. in addition, trajectory parts from turn-arounds (transition segments between flight paths over the data collection area) are cut off and the point cloud data from these parts is deleted.
This step is only active if trajectory data is available in TerraScan. The step includes and may combine the TerraScan actions Cut turnarounds and Split at laser gaps.
SETTING |
EFFECT |
|---|---|
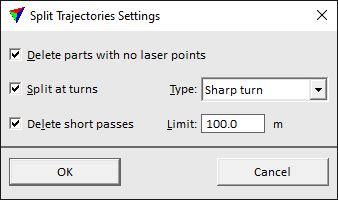
Delete parts with no laser points |
If on, trajectory parts are deleted where no point cloud data has been collected. |
Split at turns |
If on, the trajectory is split when the system flew a turn: •Sharp turn - the trajectory is cut exactly at the turn-around point. This may end up with short flight paths (transition segments) from which data should not be used. •Smooth curve - the trajectory is cut in the center of the curve. |
Delete short passes |
If on, trajectory parts and point cloud data collected for those parts are deleted if the length of the flight path is below the given Limit. Use this to remove data from transition segments between flight paths over the area of interest. |
Cut overlap step removes point cloud data from overlapping flight paths. As a result, there is data from only one flight path at each XY location. The process removes points that are closer to flight path edges (more distant from the scanner, larger scan angle) and tries to keep the data of the most central parts of flight paths (closer to the scanner, scan angle is closer to vertical). Thus, the data with the potentially biggest locational inaccuracy is removed. In addition, the data volume is reduced for further processing steps.
This step is only active if trajectory data is available in TerraScan. The step combines the TerraScan actions Deduce line numbers and Cut overlap.
SETTING |
EFFECT |
|---|---|
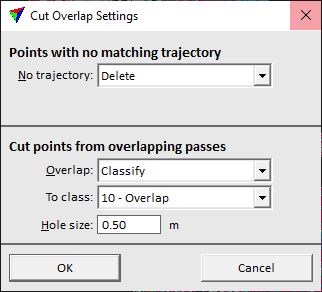
No trajectory |
Determines the action for points that can not be assigned to any trajectory: •Keep - nothing is done, points are kept as they are. •Delete - points are removed from the file. This is the default setting. •Classify - points are classified into a separate class. |
To class |
Target class for points that are not assigned to any trajectory. This is only active if No trajectory is set to Classify. |
Overlap |
Determines the action for points that are identified as overlapping points: •Keep - nothing is done, points are kept as they are. •Delete - points are removed from the file. This is the default setting. •Classify - points are classified into a separate class. |
To class |
Target class for points that are identified as overlapping points. This is only active if Overlap is set to Classify. |
Hole size |
Maximum size of an area without points that may be created by the cut overlap action. This refers to, for example, shadow areas that are not seen by the scanner in the closest flight path. If the area is larger, points from a more distant flight path are kept to fill an area. |
Smoothen and remove noise step smoothens surfaces and classifies outliers above and below surfaces as noise. Thus, it eliminates noise from the point cloud data and makes surfaces more pretty. The process uses RGB color information assigned to laser points to recognize vegetation. It may apply smoothing only to non-vegetated areas identified by the Visual-band difference vegetation index computation. If no RGB color values are usable, the points that are classified as noise close to vegetation may be later added to vegetation classes by copying the class attribute from the actively classified points.
The step combines the TerraScan actions Smoothen points and Thin points.
SETTING |
EFFECT |
|---|---|
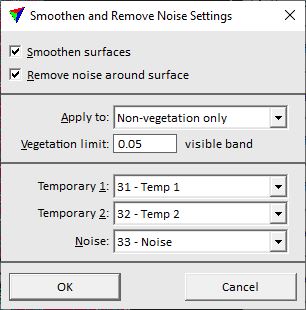
Smoothen surfaces |
If on, a smoothing process is applied to points on surfaces. |
Remove noise around surface |
If on, outliers are removed from surfaces in order to reduce noise in the point cloud. |
Apply to |
Determines the points that are effected by the process: •All points - all points on surfaces. •Non-vegetation only - only surface points in non-vegetated areas. This requires that RGB values are assigned to the points. |
Vegetation limit |
Threshold value for separating points in non-vegetated areas from points in vegetated areas by using the Vegetation index / Visual band difference method. The default value is 0.05, values may range from -1 to +1. This is only active if Apply to is set to Non-vegetation only. |
Temporary 1 |
First point class that is used for points temporarily during the process. |
Temporary 2 |
Second point class that is used for points temporarily during the process. |
Noise |
Target class for points identified as outliers. This is only active if Remove noise around surface is switched on. |
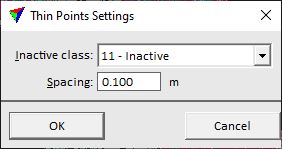
Thin points to inactive step reduces the point density by classifying many points as inactive. This is mainly done to increase the speed of further processing steps for large point clouds. Later classification steps will only consider the active points. The result of the classification in a thinned point cloud is not exactly as good as if all points are used. Therefore, this step is an option to get a classification result for large point clouds in a shorter processing time. As a last step, the above-ground object classification may be applied to inactive points by copying the class attribute from the closest active point.
The step includes the TerraScan action Thin points.
SETTING |
EFFECT |
|---|---|
Inactive class |
Target class for points that are thinned out. |
Spacing |
Distance between points that are kept as active points. |
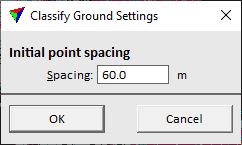
Classify ground step removes some additional outliers (such as low error points in the point cloud) and classifies the ground. The lowest (active) points are classified as ground. The process aims for a smooth ground surface represented by not too many points. Some typical flaws of the automatic ground classification are low points that become ground points and disturb the further ground classification in this area, and bridges that are often classified as ground but do not belong to the natural ground surface.
The step includes the TerraScan classification routine Ground.
SETTING |
EFFECT |
|---|---|
Spacing |
Distance between initial ground points. Basically, the setting determines the size of an area within which the lowest point is classified as ground point. From these initial points, a temporary TIN is created. Then, the ground classification process iteratively densifies the TIN by adding more and more points to the ground class. |
Check ground step is more or less a stop criteria for the processing wizard. It is a manual step where an operator checks the result of the automatic ground classification This can be supported, for example, by visualizing the ground as shaded surface, either by using the Shaded surface display mode of TerraScan (UAV) or the Display Shaded Surface tool of TerraModeler (UAV). The display tool of TerraModeler is more capable and should be preferred, if TerraModeler is available. The shaded surface display shows flaws in the ground classification quite clearly as pits (low ground points) or peaks (high ground points). Also bridges or areas of missing ground points are well visible.
Manual classification tools of TerraScan (UAV) can be used to improve the ground classification. Any change in the ground class updates the surface display automatically. The extend of the manual work is project-dependent and should include at least the removal of gross errors.
If the terrain structure is simple, the ground check may be done after all steps of the data processing wizard have been finished. If the terrain structure is complex, it is strongly recommended to do the ground check before above-ground objects are classified. Any gross errors in the ground classification effect further classification steps in a negative way.
If the Check ground step is switched on in the wizard, all following steps are deactivated.
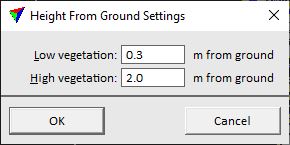
Classify height from ground step classifies points above the ground into three "vegetation" classes:
•Class 3 Low vegetation - points < 0.3 m above ground
•Class 4 Medium vegetation - points 0.3 - 2.0 m above ground
•Class 5 High vegetation - points > 2.0 m above ground
The height limits can be changed in the settings for the step. The step has an active use only if above-ground objects are further classified. Points in classes 4 and 5 are considered for the object classification.
The step combines the TerraScan actions Compute distance and Classify by distance.
SETTING |
EFFECT |
|---|---|
Low vegetation |
Limit for points in class 3 Low vegetation. Points with a smaller height above ground are classified as low vegetation. |
High vegetation |
Limit for points in class 5 High vegetation. Points with a larger height above ground are classified as high vegetation. |
Classify above ground features
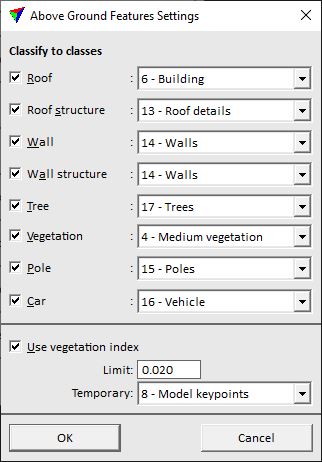
Classify above ground features step classifies points in classes 4 and 5 into up to 8 object classes. The processing step includes point cloud segmentation (grouping in TerraScan) and a group classification based on best match principle. The user may decide which object types are of interest for a project. It is recommended to switch on a few object types for the classification as the routine is based on probability comparison.
The step relies on the Classify height from ground step and is only available, if this step is active or has been performed. The classification may benefit from vegetation index computation if color values are available for the laser points.
The step combines the TerraScan actions Assign groups and Classify groups by best match.
SETTING |
EFFECT |
|---|---|
Roof |
If on, groups of points that represent horizontal or sloped planar surfaces without ground points underneath are classified to the given class. Typical objects are building roof planes. |
Roof structure |
If on, groups of points that represent small structures on roofs are classified to the given class. Typical objects are chimneys, antennas, air condition constructions, etc.. |
Wall |
If on, groups of points that represent close to vertical planar surfaces are classified to the given class. Typical objects are building walls or any other type of wall. |
Wall structure |
If on, groups of points that represent small structures on walls are classified to the given class. Typical objects are balconies or other constructions on (building) walls. |
Tree |
If on, complex groups of points with a bigger height above ground and a wider horizontal extend are classified to the given class. Typical objects include trees. |
Vegetation |
If on, groups of points that do not fit to any other object type are classified to the given class. This often includes lower vegetation or other structures. |
Pole |
If on, groups of points that represent narrow high structures are classified to the given class. Typical objects are street lamps and poles of overhead traffic lights, street signs or wires (not power line towers). |
Car |
If on, small compact groups of points with a lower height above ground are classified to the given class. Typical objects include cars. |
Use vegetation index |
If on, the process uses the vegetation index computed from color values of points for separating vegetation from non-vegetation objects. |
Limit |
Threshold value for separating vegetation from non-vegetation. The default value is 0.05, the values may range from -1 to +1. A good value for a point cloud can be found by using the display mode option and testing different limit values in the Point display category of TerraScan Settings. |
Temporary |
Point class that is temporarily used for vegetation/non-vegetation points during the process. |
Copy result to inactive points
Copy result to inactive points step copies the class attribute from the closest active point to points previously thinned out as inactive. This is only required if the Thin points to inactive step has been performed in order to speed up the classification processes. It should be applied to points of above-ground objects.
The step includes the TerraScan classification routine Closeby points.
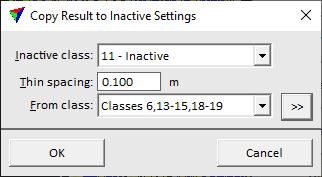
SETTING |
EFFECT |
|---|---|
Inactive class |
Class the contains the previously thinned out points and is now effected by the process. |
Thin spacing |
Distance used for thinning out points. |
From class |
Source class(es) to copy the class attribute from. |
|
Opens the Select classes dialog which contains the list of active classes in TerraScan. You can select multiple source classes from the list that are then used in the From class field. |
Copy result to noise points step copies the class attribute from the closest active point to points previously classified as noise. This is only required if noise was classified in the Smoothen and remove noise step. It should be applied to points of above-ground vegetation objects, such as trees or other vegetation. Noise points close to surfaces should remain in the noise class.
The step includes the TerraScan classification routine Closeby points.
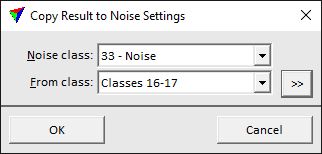
SETTING |
EFFECT |
|---|---|
Noise class |
Class the contains the previously classified noise points and is now effected by the process. |
From class |
Source class(es) to copy the class attribute from. |
|
Opens the Select classes dialog which contains the list of active classes in TerraScan. You can select multiple source classes from the list that are then used in the From class field. |