Compute normal vectors
Compute normal vectors command can be used to compute and store two additional attributes for laser points, a dimension and a normal vector.
The software determines the dimension of each point by analyzing the point and its closest neighbour points. There are three types of dimensions:
•Linear - points form a linear feature.
•Planar - points form a planar surface.
•Complex - random group of points.
The normal vector is computed for points of planar dimension. It is strongly recommended to have trajectory information available for computing normal vectors for mobile ground-based laser data. However, the process also runs without trajectory information which may give good results for airborne data sets.
The attributes can be used for the visualization of points and for classifying points. For instance, points on a road surface in an MLS data set can be classified By normal vector in order to detect locally flat places. In ALS data, the normal vector can be utilized to analyze roof structures.
The dimension and the three components (XYZ) of the normal vector can be stored in TerraScan FastBinary files.
To compute normal vectors:
1. Select Compute normal vectors command from the Tools pulldown menu.
This opens the Compute Normal Vectors dialog:
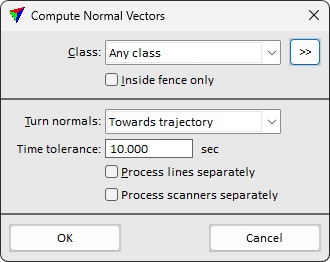
2. Define settings and click OK.
This starts the computation process. It assigns a dimension value to all laser points and a normal vector to all points of planar dimension. An information dialog shows the number of points for which a normal vector has been computed.
SETTING |
EFFECT |
|---|---|
Class |
Point class(es) for which dimensions and normal vectors are computed. |
|
Opens the Select classes dialog which contains the list of active classes in TerraScan. You can select multiple source classes from the list that are then used in the Class field. |
Inside fence only |
If on, normal vectors are computed only for points falling inside active fence or selected polygon |
Turn normals |
Defines a target point for the normal vector direction: •Towards trajectory - turned towards the trajectory position. This requires trajectory information available in TerraScan. This is the preferred method for airborne and mobile point clouds. •Towards center point - turned towards the center point of the point cloud. This is suitable for static terrestrial point clouds. •Upwards - turned to upward direction. Suited for airborne point clouds if no trajectory is available. •Towards vectors - turned towards a selected vector element. This is suitable for mobile point clouds of tunnels or other inside scans if no trajectory is available. It requires that a 3D line string is drawn inside along the tunnel center and selected before the tool is started. |
Time tolerance |
Maximum difference in time stamps of points that are considered for calculating the normal vector. |
Process lines separately |
If on, the dimension and normal vector computation is done for each line separately. This is recommended if the data of different lines do not match to each other. |
Process scanners separately |
If on, the dimension and normal vector computation is done for each scanner separately. This is recommended if the data of different scanners do not match to each other. |
